What Does HTTPS Do?
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. In simpler words, it secure the “interactions” between a user and web. It is the “primary” protocol for the transformation of information across internet.
Ever since the internet became more accessible, users have become more immersed in the Web. On the good side, it gets more user interaction; on the bad side, the hackers become more vulnerable.
Although HTTPS was created in 1994, but users were unaware of its importance till last decade. Now, HTTPS is a ranking signal on Google. Do you know that?
There is a psychological fact that if something is easy to access, at least 20% of users will use it in a bad way or exploit it. Your web informations are easily accessible and that’s why they are at the risk of exploitation. And that’s where hackers are born!
I’m not saying hackers are bad. Many hackers operate legally, like White-hat hackers. They engage in hacking to improve digital security. These white hackers are considered authorized hackers. Like them, there are many:
- Black hat: An illegal and criminal one who tries to steal users’ information without their consent. These are the one who steal your information id HTTPS are not integrated on your website.
- Gray hat: They are illegal too but their intentions are non-malicious. In other words, they are “just for fun” hackers.
- Green-hat: They are novice or beginner-level hackers who can turn to white or black hat.
- Red hat: Government-hired hackers, also known as vigilant hackers. Their duty is to restrict and stop black hat activities, and they are knowledgeable about black hat strategies.
- Blue-hat: Authorized software hackers who can be anyone they like green hat, white hat, or even red hat.
Thus, if HTTPS is not used on your website, there is a chance of Data Interception, Information Theft, Man-in-middle attacks (hacking), and losing customers due to a lack of trust.
You create a website to get more customers, users, trust and to build a community. Right? But if you are not using HTTPS all is vain.
Therefore, today, we will see the statistics about HTTPS on the Web; these numbers and facts will be mind-blowing.
After knowing these facts and stats you will never ignore the importance of HTTPS.
Get ready to receive loads of value.
Why is HTTPS a must?

85.1% of all websites on Google use HTTPS as default protocol. They use it as a shield for their website so that competitors and hackers can’t breach their web activities. But it goes beyond safeguarding behavioral and identification information from potential trackers.
A user (or visitors on your website) feel more secure after knowing that all communications between the browser and the server are encrypted via SSL/TLS authentication. Because of this security they visit your site frequently.
The broader support for HTTPS by major browsers like Google Chrome, Edge, and Mozilla Firefox, with features like HTTPS-only mode, is an added advantage.
HTTPS positively impacts a website’s search engine ranking. The introduction of HTTP/2 in 2015, focusing on HTTPS, has accelerated web browsing and pushed website owners to transition. It ensured safer and more efficient online landscape for users.
How does HTTPS work?

Before moving to the HTTPS stats, it’s essential to understand how HTTPS works and on which Layer these processes are happening.
As we all know, HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. If an HTTP is integrated on a website it means that the communication via computer networks is secure. It signals the visitor that the site is secure to access and protects the confidentiality and integrity of the data transmitted.
Now, how does it work? I’m not taking a CCNA or CCNP class today; it’s essential to understanding how HTTPS works and which Layer of the OSI model (7 layers) is used.
For better understanding, let suppose you are accessing our website Socialmarketing90 as a user. Let’s see how HTTPS runs here.
Step 1: When you visit the SM90 website, your browser creates a secure connection with the web server. In other words, it’s an SSL/TLS handshake.
Step 2: Since the SM90 holds HTTPS, the server and the browser exchange information, including SSL certificates, where the public key of the server is contained.
Step 3: Here comes HTTPS’s work, which uses asymmetric encryption through a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). The server’s public key, included in the SSL/TLS certificate, is used by the browser to encrypt data sent to the server. The server then uses its private key to decrypt the data.
Step 4: Now the secure connection is enabled, so the browser and the server start the data transfer. Which means the browser will encrypt the data before it sends it to the server (Receiver end). The server will decrypt the data once received. Here is where the Application layer and Transport layers are used.
Step 5: Even though the data transfer is happening, these SSL/TLS will secure the data transferred. It means it cannot be read or tampered with by any third party, providing confidentiality and integrity.
Step 6: So that’s the end of the session. Once you complete browsing the SM90 page, the session keys used for encryption are discarded, ensuring that each session is uniquely encrypted. This process will repeat endlessly whenever the users access the website.
Check the image below for visual understanding.
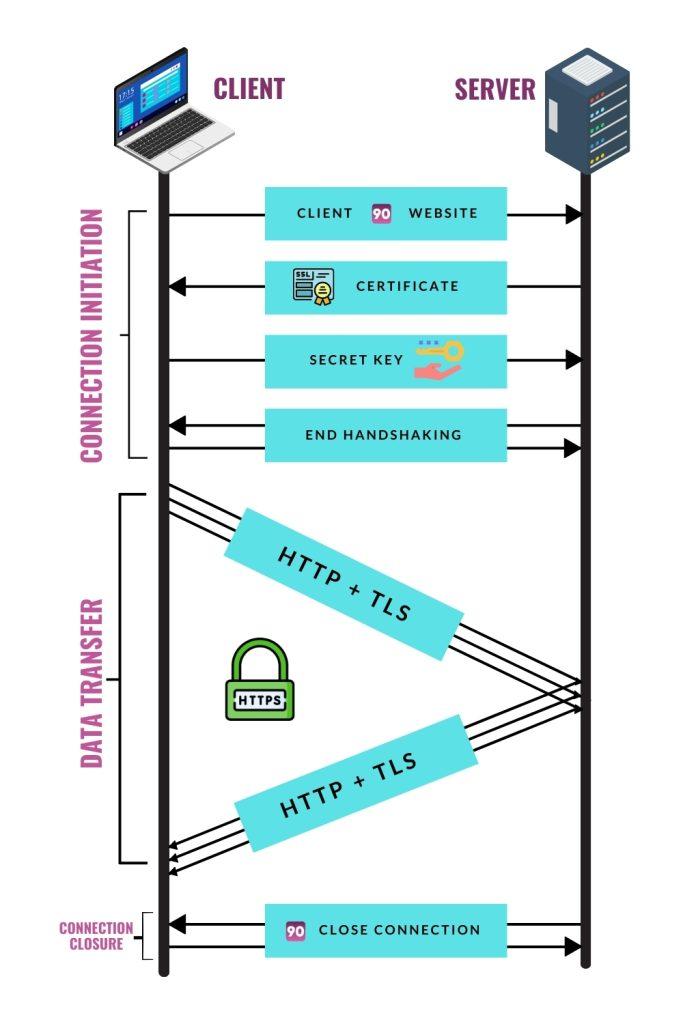
All this happens in the Application Layer (7th Layer) and Transport Layer (6th Layer) on the OSI Model.
So, now I think you have sufficient knowledge about HTTP and you’re good to go for stats.
Keep reading!
12 HTTPS Statistics on the Web

1: HTTPS was first proposed by Netscape Communications in 1994

Netscape communications introduced HTTP in 1994 to secure the online transactions for their web browser, Netscape Navigator.
The founder of HTTP is Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee aka TimBL.
2: 98.1% of the top 1 million websites support HTTPS

HTTPS encrypt sensitive information of the website which ensure safe browsing.
It means that every website should adopt HTTPS with TLS/SSL certificates for a secure browsing experience.
3: Did you know that 93.2% of browsing time on Google Chrome browser is spent on HTTPS websites?
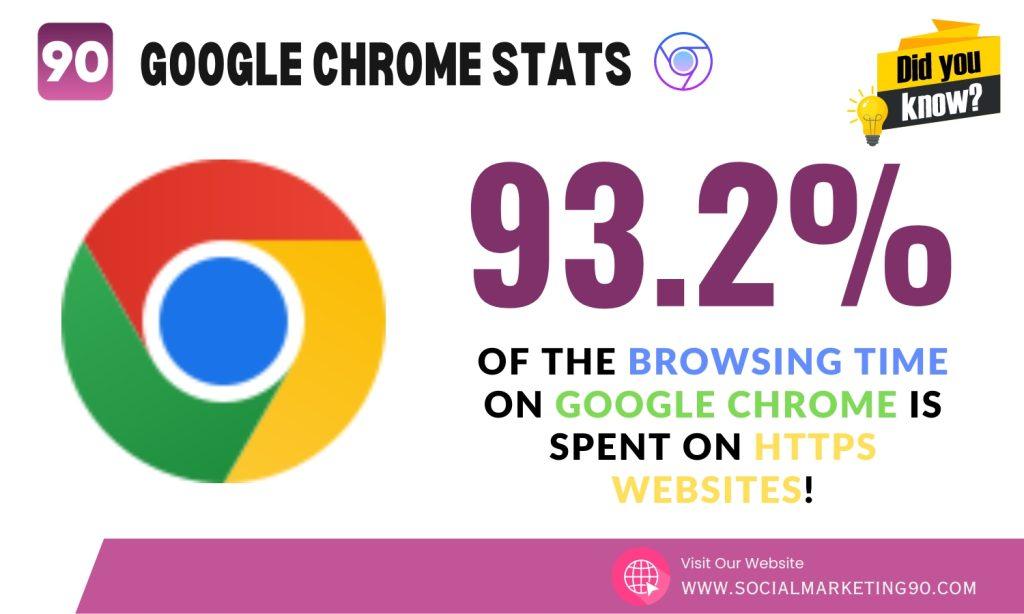
This information comes straight from Google’s Transparency Report.
And the best part? HTTPS doesn’t have any performance issues. TLS/SSL certificates bring a lot of performance enhancement capabilities to websites. If you want to boost your website’s performance, always use HTTPS with TLS/SSL certificates.
4: According to “Lets Encrypt Research,” around 81.1% of Firefox webpages use HTTPS!
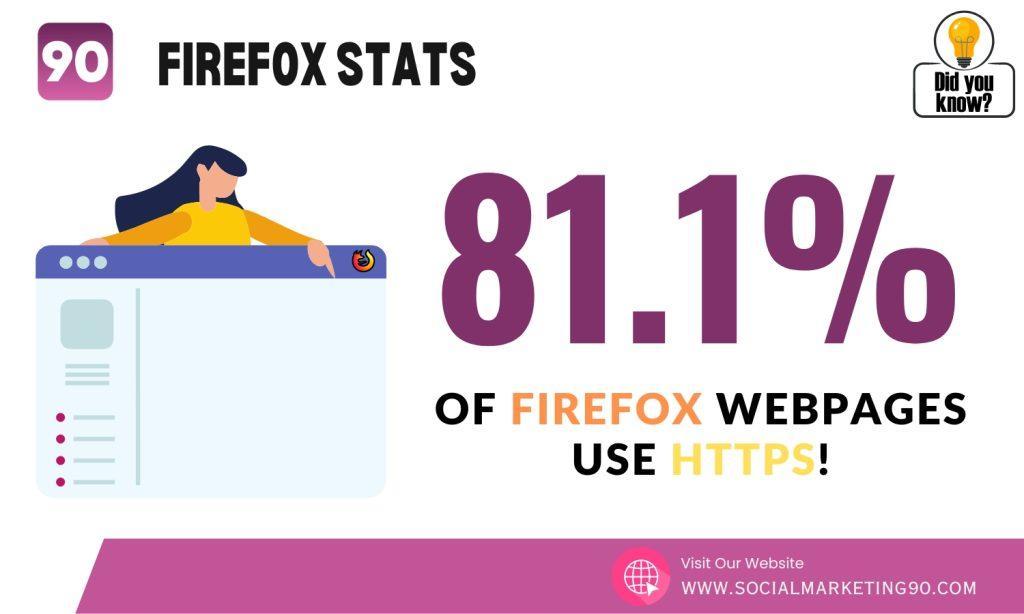
This means most websites are taking essential steps to protect your online security and privacy. Using HTTPS, websites ensure that sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details, is encrypted and safe from potential hackers.
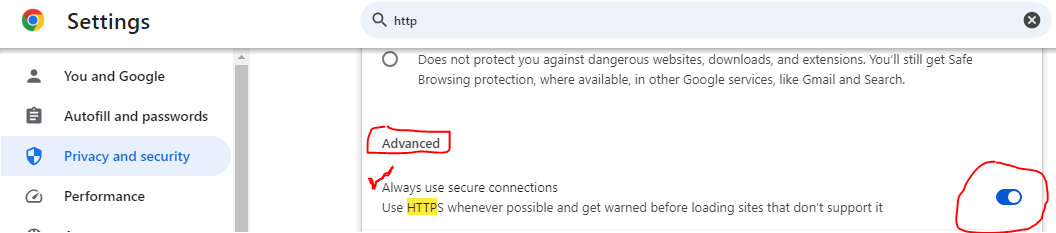
Users can also enable HTTPS secure browsing through Google Chrome. Go to your chrome’s setting. Search “HTTPS” in search bar, scroll a bit down, check in “Advance” and enable “always use secure connections”
5: As per W3Techs, 85% of websites use the default protocol HTTPS
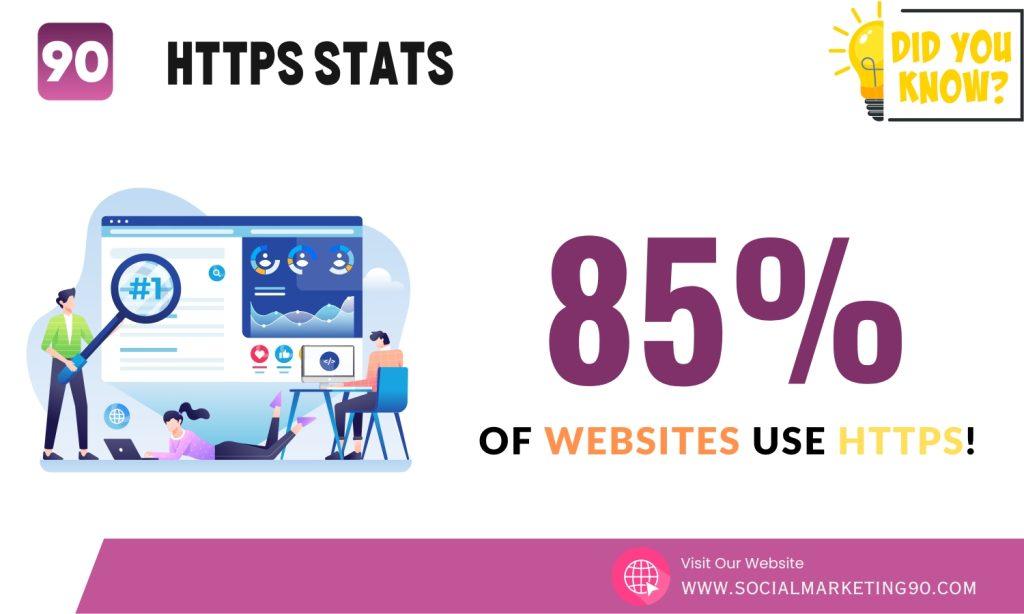
85% is a huge figure, and it clarifies that using HTTPS is no longer just a recommendation but a necessity to ensure the safety and security of your website’s visitors.
4: According to Google's Transparency Report, almost 93% of web pages are loaded over HTTPS in Google Chrome
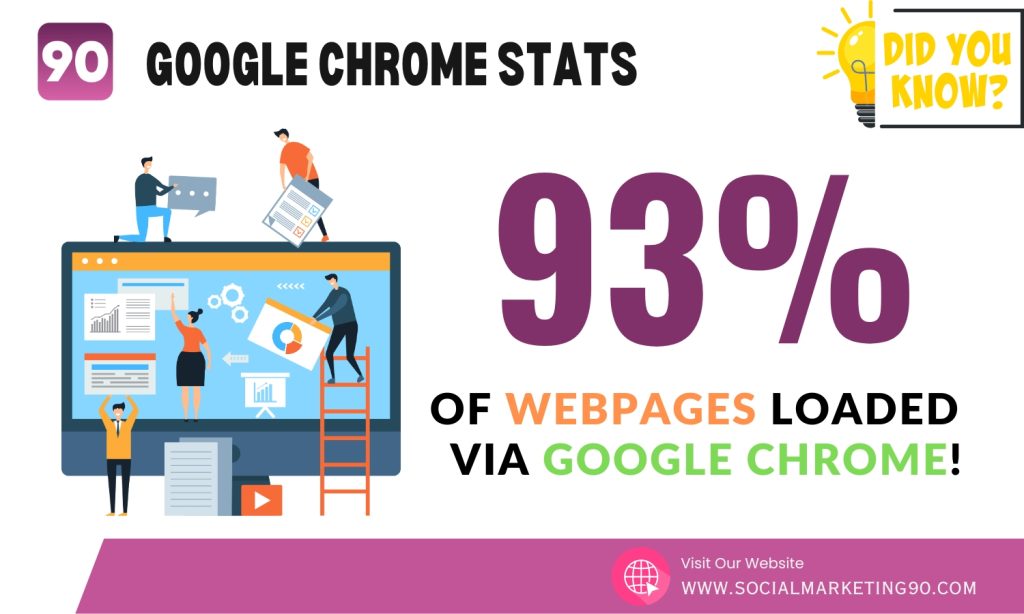
That means 93% visitors have enabled HTTPS safe browsing. If your website does not support HTTP, you are loosing 93% of traffic.
7: According to Google's transparency report, on January 6, 2024, 97% of the web pages loaded on Chrome in the United States were secured with HTTPS.
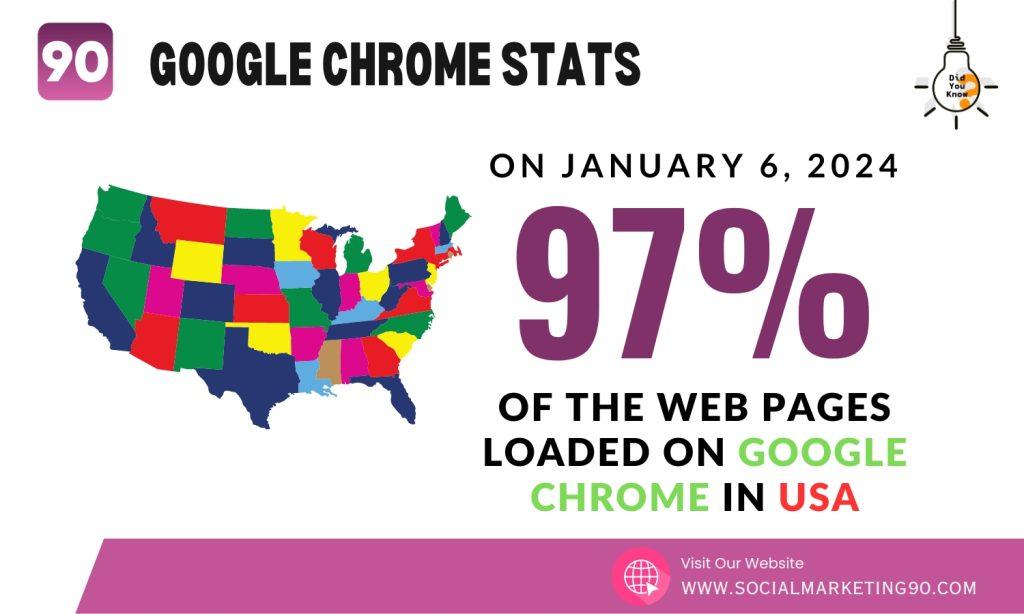
This is a significant improvement in internet security, as HTTPS encrypts the data between the website and the user. It prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information. This positive trend towards more secure internet browsing experiences reflects the growing awareness and importance of internet privacy and security among users and website owners alike.
9: According to the Google Transparency Report, out of 100 sites, 97 are using HTTPS as the default protocol.
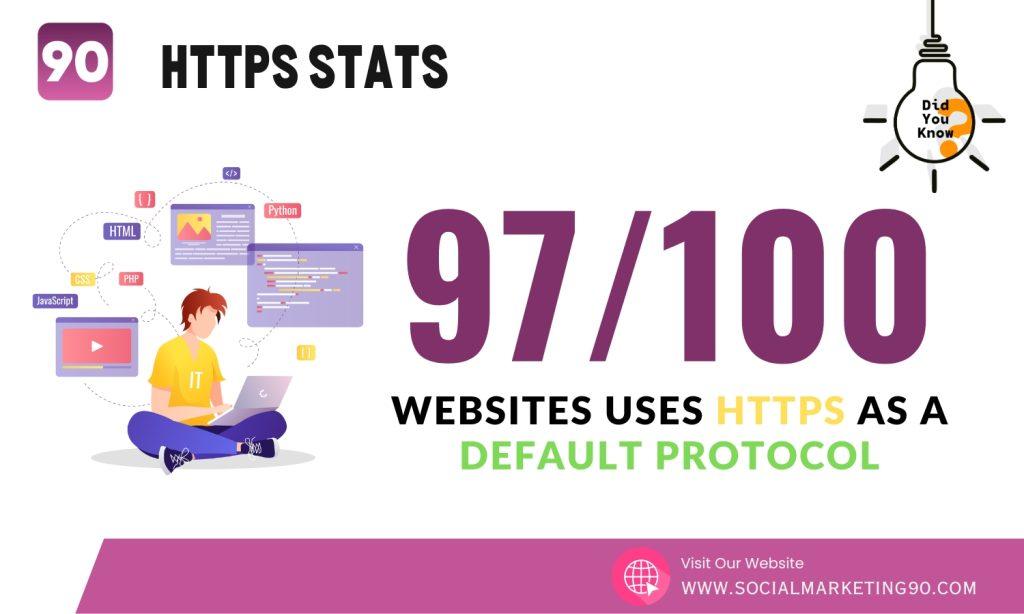
This proves that website owners are taking the necessary steps to protect their users’ data and ensure their online safety.
This step makes them credible and help them get more ranking.
9: Belgium is the 1st country with 99% of traffic to Google, which is encrypted.
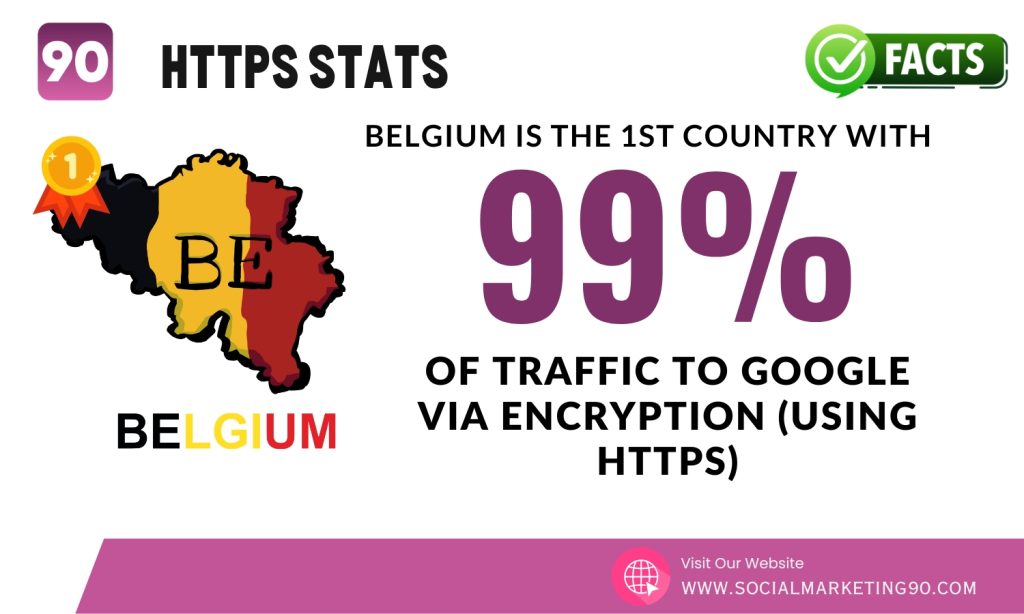
Sounds like Belgians are the most cautious people. Any data transmitted between Belgian internet users and Google is protected from prying eyes and potential cyber threats. With such a remarkable achievement, Belgium is leading towards a more secure and trustworthy online experience.
10: Did you know that HTTPS URLs use port 443 by default?
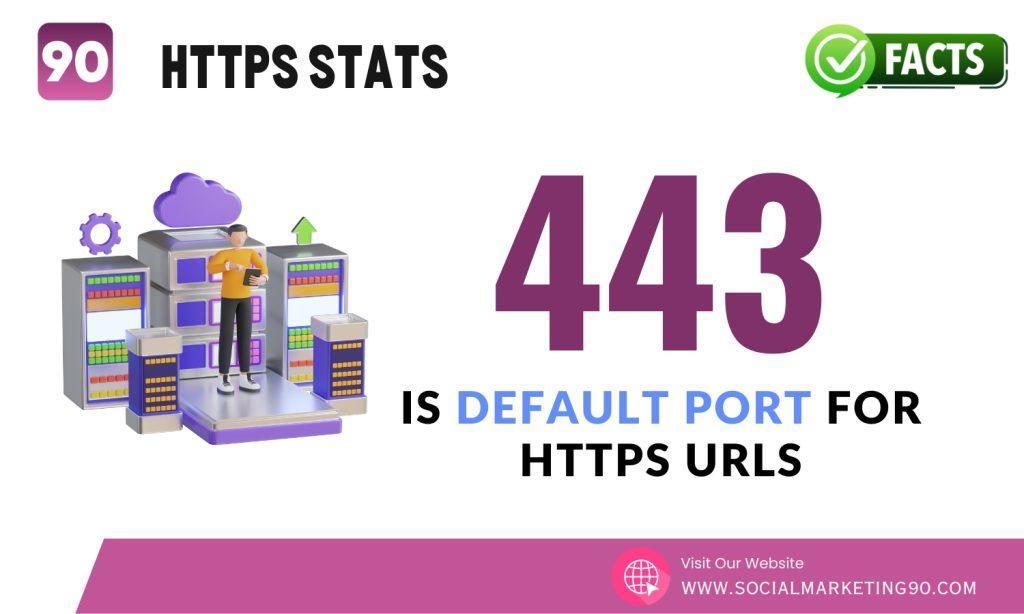
It’s important to remember this when setting up secure connections for your website or online services. If you don’t set it correctly the user will get “Port 443 error” message.
Keep this in mind to ensure safe and reliable communication with your users.
11: Google considers HTTPS a ranking signal

HTTPS is a “credibility” factor. So using HTTPS helps websites rank higher on Google search results.
Thus, ensure your website uses HTTPS to stay ahead of the competition and attract more visitors.
12: HTTPS uses TLS or SSL cryptographic protocols to establish a secure browser and server connection.
Cloudflare says over 90% of internet traffic is now encrypted with HTTPS. Using HTTPS, websites can ensure sensitive information is safe from potential hackers.
Using HTTPS also helps websites rank higher on Google search results. So, ensure your website uses HTTPS to provide users with a safe and competitive browsing experience.
Wrap Up

Users are the king of the internet. If there is no one to access the internet, then there is no use in improving security. These statistics and details of HTTPS are an eye-opener for beginners.
You can always save this blog as a beginner guide if you’re going to start a website or a blog site.
Having a secure and confidential connection is the cue card. It’s just like saving money in a bank!
Since HTTPS is mandatory, many hosting/website building services provide free SSL certificates; some of them are;
- Asura Hosting (web hosting)
- Hostinger (web hosting)
- Web.com (hosting and website builder)
- CodeDesign AI (hosting and website builder)
- Bluehost (web hosting)
That’s the wrap for the day, guys! I’m always here to answer your queries if you need any further information about HTTPS and SSL/TLS. Stay tuned for another nail-biting Stats blog!